Logical Drug Design: A Structure-Based Approach
Kirk D. Wyatt, Amanda M. Hanks, Mehreteab Y. Mengsteab, Christopher T. Adams
The principle underlying logical drug design–the utilization of structural cues in order to arrive at drug candidates–is both efficient and elegant.The adoption of this new paradigm in the field of pharmacology–which has been greatly accelerated by advances in X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy–has led to the development of a countless number of pharmaceuticals. In keeping with the structure-focused nature of logical drug design, the following JMol tutorials offer a sampling of the key structural features of four proteins that have been the targets of logical drug design.Combination Therapy with Allosteric and Competitive Inhibitors of the Abl Kinase
Kirk D. Wyatt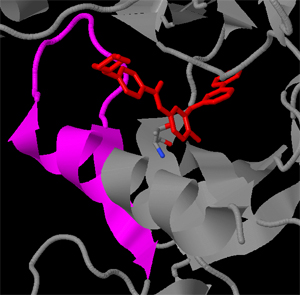
The Abl kinase is involved with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) which is a form of cancer that affects white blood cells. Inhibitors of Abl have been developed, through logical drug design, as pharmacotherapeutic treatments of CML; however, the emergence of mutant forms of the kinase has rendered the drug ineffective in many patients. In this JMol tutorial, we will explore some of the key structural features of Abl. We will explore a mutation that occurs within the active site and examine a mechanism for allosteric inhibition that can overcome the drug resistance conferred by this mutation.
Sertraline inhibition of LeuT: a bacterial analogue to mammalian serotonin transporter SERT
Amanda M. Hanks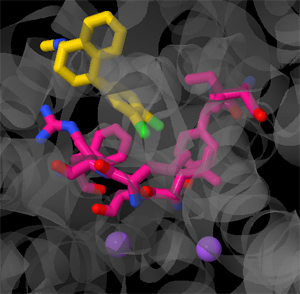
Sertaline is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that is used as an antidepressent medication. A product of logical drug design, it inhibits the presynaptic plasma membrane serotonin transporter (SERT). In this JMol tutorial, we will explore the important structural features of SERT and investigate the specific residues that are involved with the drug-protein interaction.
Fluticasone Propionate
Christopher T. Adams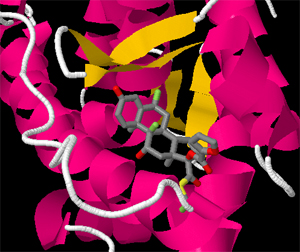
Fluticasone propionate mimics the natually-occurring hormone cortisol which, upon binding to clucocorticoid receptors, causes anti-inflammatory responses. The ligand-glucocortocoid complex binds directly to DNA in order to regulate the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory proteins. In this JMol tutorial, we explore the mechanism by which fluticasone propionate binds to the glucocortocoid receptor.
Raltegravir: a logically-designed inhibitor of PFV Integrase
Mehreteab Y. Mengsteab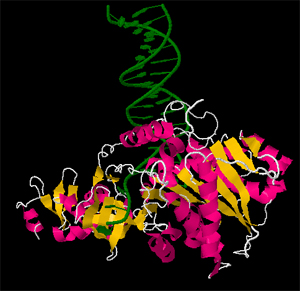
Raltegravir is a antiretroviral drug used to treat HIV intfections. Raltegravir is the first of a new class of antiretrovirals which act as integrase inhibitors. Insofar as integrases play a crucial role in the integration of viral DNA into the genome of the host cell, integrase inhibitors are able to block this crucial step in the viral life cycle and prevent further viral replication. In this JMol tutorial, we explore PFV integrase bound to viral DNA, raltegravir and a magnesium cofactor.